In Academic Publishing, there are many solutions for managing the production of Journal articles; here we focus on high-quality production; with “High-Quality” we mean that it is necessary the interaction between the Scientific (the Scholarly Community) AND the Publisher.
High quality requires that each article should be published in many formats, and the creation of rich metadata to disseminate. How to achieve these requirements?
I present here 4 different workflows; each could involve or not the use of a single or more platform to manage a single or all the phases involved; the focus to categorize them is analyzing which tool is used to manage the Fulltext content of the article (or book).
I find 4 main workflows.
- Classic – it uses Adobe Indesign as the tool
- Manual – it uses MS Word and an XML editor / converter
- LaTeX – It uses LateX or TeX or similar
- XML workflow – It uses a platform (XML) to manage content
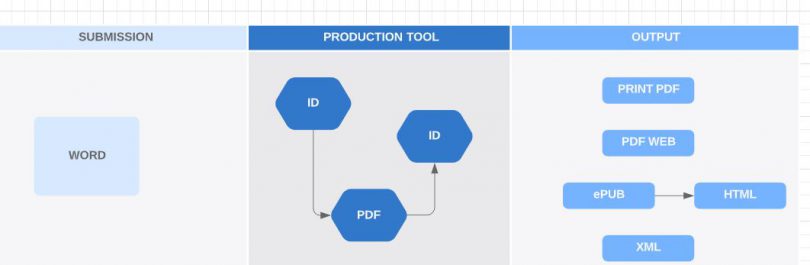
- Classic workflow
Here the Classic workflow: the manuscript file is managed by the publisher, using Adobe Indesign. The outputs are extracted from Indesign. It needs an extra work of tagging to generate valid HTML or XML output.
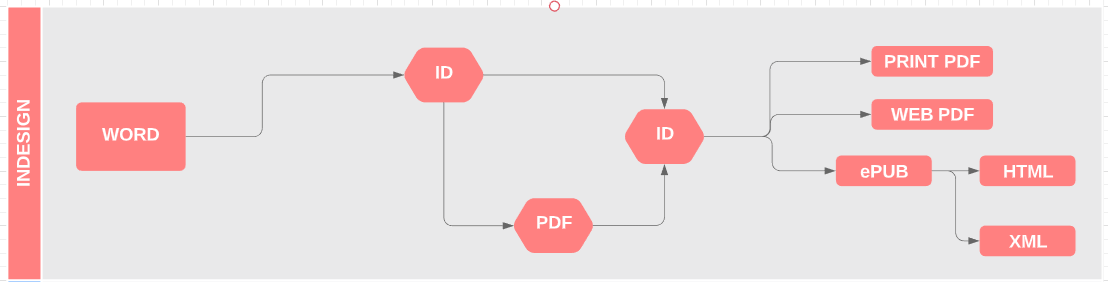
2. Manual workflow
Here the Manual workflow; the primary source of content is managed by MS Word; then someone (outsourcing in India, China or the Philippines) manually produce XML JATS + Metadata. From these, there is automatic conversion to other formats.
Sometimes, the MS Word is converted in HTML (or other tagging suite/standard such as Markdown, YAML, RASH…). All these cases require an high-specialized and no-standardized manual work to get high-quality output.
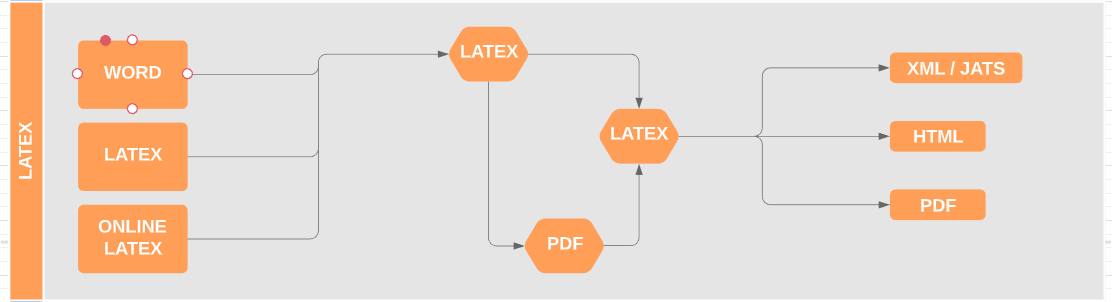
3. LaTex workflow
LaTex is used as the main content format all along with the production; at the end, there is automatic conversion to other formats, with some small extra work.
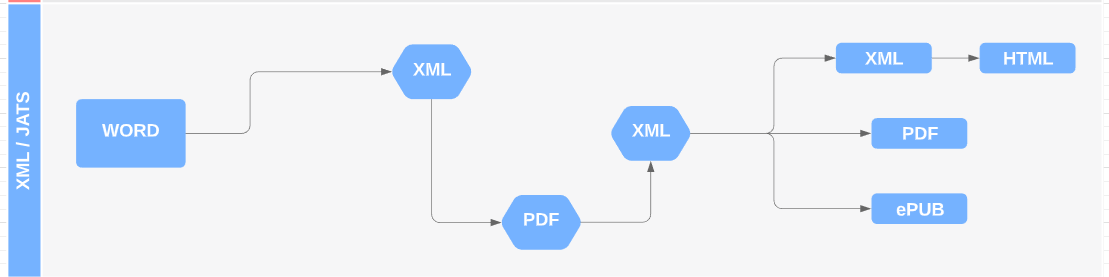
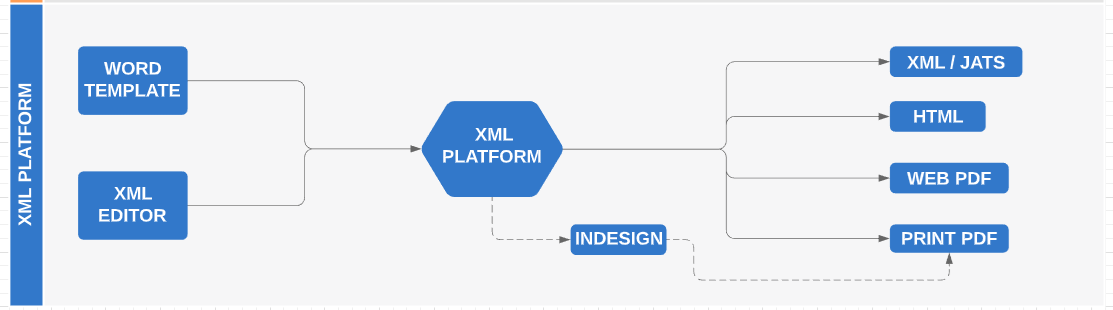
4. XML platform workflow
This is the most complex workflow. Using a platform (from the beginning, or after submission by a conversion) the content is managed by using XML through a web platform. In some cases there is an Indesign plugin to export content to Indesign, to generate Print PDF.